Set up a quality and accountability assurance system for the response
The WASH response must be coordinated not only to maximise outputs and beneficiary reach, but also to make real progress towards objectives and ensure response is safe, inclusive, participatory and effective. Coordination platform can address this by setting up and following up a Quality Assurance and Accountability Systems (QAAS). A QAAS is a process implemented at national level that aims at ensuring standards for quality and accountability in humanitarian WASH responses are met and maintained, with continuous improvement. It provides a way to monitor the WASH response against a jointly agreed, contextually relevant quality and accountability framework. An effective QAAS is the joint responsibility of the Cluster Lead Agency, the Cluster Coordinator, Cluster partners at national and subnational level and donors. As humanitarian response will always face external constraints, the aim of a QAAS should be to provide the highest quality possible in the context by making improvements over time, rather than reaching an absolute level of quality. The QAAS comprises:
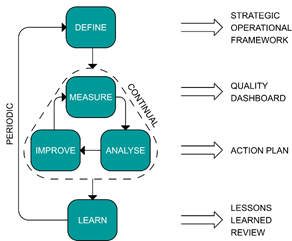
- A Guidance Note describing the steps required for National WASH Clusters to set up routine systems for quality assurance and accountability within the humanitarian programme cycle. This involves a systematic and collective process of setting up quality benchmarks, quality monitoring, taking action to address issues and learning for continuous improvement. This process is summarised in the diagram on the right and in the below table.
- A modular analytical framework that defines core standards, indicators and monitoring approaches that should be used to routinely monitor quality and accountability. Current modules are 'Public Health Risk', 'WASH service provision', 'People-centered programing', 'Market awareness and market based programing';
Figure 1: The QAAS process and Key Outputs
| STEP | DESCRIPTION | OUTPUT | TIMING |
|---|---|---|---|
1. DEFINE | The WCC convenes a TWiG. The TWiG choses the most appropriate modules of the modular analytical framework, set Key Quality Indicators (KQI) benchmark, agree on timing, approach and roles for data collection, reporting and analysis. | QAAS definition within the Strategic Operational Framework (SOF) validated by the SAG |
|
2.MEASURE | KQIs are continuously monitored by cluster partners and Third Party Monitors. Data is reported to the cluster IMO who produces Quality snapshots. | Continuous measurement, analysis and improvement through regular coordination meetings; ad-hoc alerting of priority gaps. | |
3.ANALYSE | Quality Snapshot shared by IMO with cluster partners; quality gaps are prioritised; Action plans for addressing gaps are developed by the . | Action plan | |
4.IMPROVE | Action plans are implemented by partners and monitored by the TWiG; Information about issues identified and action plans is fed back to the affected population | Corrective actions Feedback to the affected population | |
| 5.LEARN | Trends, monitoring data and action plans are periodically reviewed by the TWiG; lessons learned are produced by partners including the CLA; SOF is revised accordingly by the SAG | Updated QAAS / SOF Lessons learned disseminated to GWC partners, decision makers and donors | Periodically
|
Table 1: The QAAS process and Key Outputs