...
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
...
Estimate the overall WASH response funding
...
requirements
The HRP is also a funding funds raising appeal document, where funding requirements of each cluster are presented separately and consolidated to form the total funding requirement for the response. Each sector coordinator is responsible to estimate the budget needed to implement the sectorial strategy for the coming year/phase. This is a complicated task : as many parameters must be considered, and many variables are still unknown during planning phase (material cost, logistic cost...), which can change the overall budget. Nevertheless, response costing must be done quickly enough for funding to be allocated without delay. Even if estimations are roughwhen costs are roughly estimated, it is important to be transparent and be able to explain later how figures were it was calculated. Cluster response budget also represents a target, budgets also represent targets against which funding allocation level will be regularly measured; funding monitoring figures are used as an advocacy tool in case of insufficient funding level. Such monitoring of the funding status is used to advocate for further efforts in resource mobilization throughout the response.
| Response costing method |
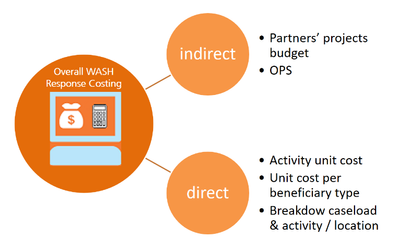
As defined shown in the diagram above, there are two ways for WASH Cluster coordinator coordinators to estimate WASH response budget:
1- Indirect costing: In protracted emergencies , in (usually around September), partners are requested to summarize and upload a summary of their planned projects for the next year on the OPS website. Cluster coordinators can be asked to pre-validate their project making projects on OPS to make sure they meet minimum criteria. Operational Response Plan’s cost costs can be calculated by adding up requested budgets from all approved partner’s planned proposals. This method can be used in sudden onset emergenciesThe positives and negatives aspects of this method include:
- Pros:
...
- quick,
...
- participatory; field oriented
...
- ; partners can in theory factor in their capacity
- Cons: can be very inaccurate because:
-Partners have tendency to overestimate their funding requirements, and do not necessarily factor in difficult access and , or their capacity gap
-Difficult to estimate geographic/program overlapping. Partners will not do it between themselves, as they are anyway in competition for funding
-Subjective, based on partner’s estimation
2- Direct costing: WCC The WASH Cluster coordinator use caseload figures, priority activities and unit prices costs to estimate total response budget him/herselfthemselves. Activities/beneficiaries' unit costs can be estimated directly, or taken from partners’ former projects’ final report (final reports’ budget are indeed preferred to proposal ‘s budget, as cost costs are usually more accurate).
- Pros: apparent accuracy. ; Can provide further guidance to partners’ proposal evaluation in terms of unit cost. ; Help to evaluate future projects' cost. Based on population figures/caseload, so access and capacity already factored in.
- Cons: time consuming for HWCP, cluster cooridnators; based on population figures that are sometimes inaccurate , not participative. Unit cost can be only approximative; not participatory ; unit cost are usually only approximate, and vary from one place to another.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
| Tip | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
OPS (Online Project System), where cluster partners are requested to upload a summary of their planned project for next year |